What is Aperture ?
My own analogy for aperture is as a window. Let us imagine for a moment;
Imagine you're sitting in a dark room, and you are facing on a wall that has five small windows. What do you see then? surely you can not see clearly the contents on the room.
Now you open a window and let the sunlight coming through the window.
Today you begin to see the contents of the room in a faint. Then you open two windows next, of course, the room will be bright.
And you are able to identify objects around the room where you sit. When you open all the five window , then the room will really light, and you can see clearly objects that exist in the room.
That is an example from me to describing an aperture as i imagine. Well in some text book or from another people which knowing better than me ,The aperture is measured in f-stops,and each stop represents a factor of two in the amount of light admitted.
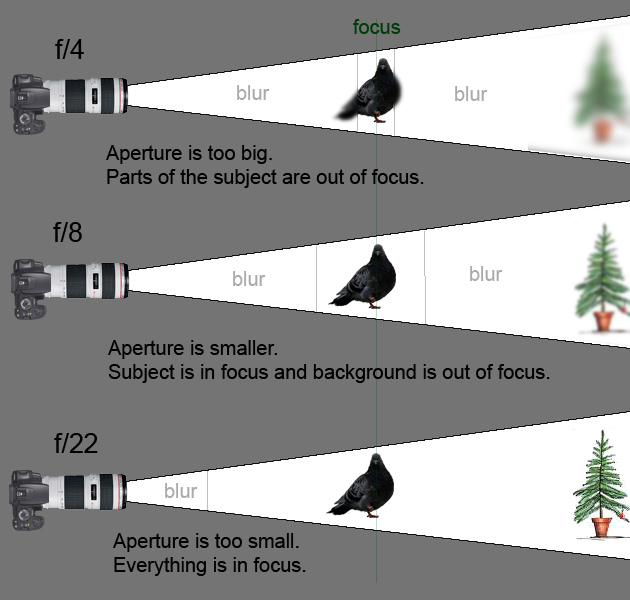
The aperture setting (f-stop), combined with the focal length of the lens, determines the depth of field of an image.

f-stop
The photographer adjusts the opening of the aperture by setting the f-stop. An f-stop is a ratio of the focal length of the lens to the diameter of the opening of the aperture.
For example, a 50 mm lens with an aperture opened up to a diameter of 12.5 mm results in an f-stop of f4 (50 ÷ 12.5 = 4).
Therefore, the larger the numerical value of the f-stop, the smaller the opening of the aperture. The speed of a lens is determined by its largest f-stop value (smallest number). Thus, the larger the aperture, the faster the lens.
Here are some basic tips about f-stops:
- As a general rule, f/5.6 gives a little bit of depth of field, provided the lens focal length isn’t too long, and is still wide enough to enable high shutter speeds.
- If it gets really dark, don’t be afraid to open your aperture to its maximum aperture, for example, f/2.
- If you need loads of depth of field, or you want a slow shutter speed, stop down to f/11 (when using a short lens) or f/22.
If your picture looks a little bit lighter or darker than it should, take another, having adjusted the exposure. You can make your image lighter by decreasing the number of f-stops, or darker by increasing it.
Note:
Focal Length ; The distance from the principal point from inner lens to the focal point of the image sensor.
f/stop ; The numerical expression of the relative aperture of a lens. Each f/number is 1.4 times larger than the preceding one, and each number indicates a halving or doubling of the amount of light allowed to pass through the lens.